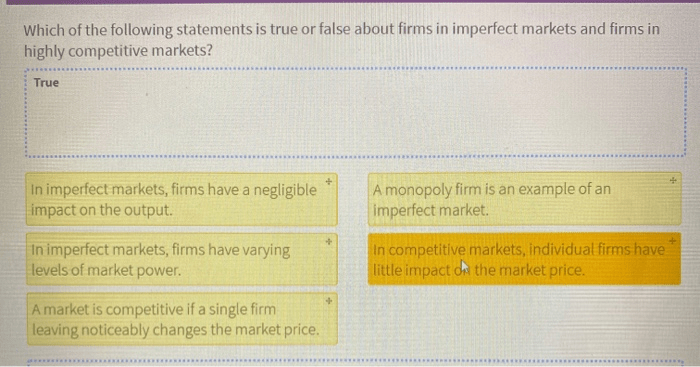
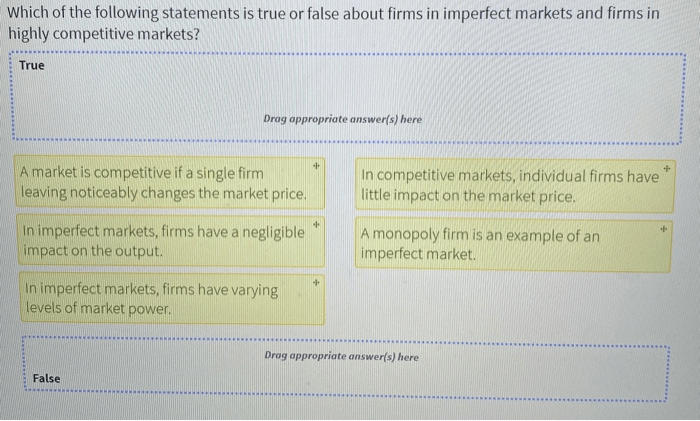
Which of the following statements is true of markets? This intriguing question embarks us on a captivating journey into the intricate world of markets, where we delve into their fundamental concepts, dynamic forces, and potential shortcomings.
Markets, as we shall discover, play a pivotal role in shaping our economic landscape, influencing prices, consumer choices, and even societal well-being. By unraveling the complexities of markets, we gain invaluable insights into the mechanisms that govern our economic interactions.
Market Fundamentals
Markets are venues where buyers and sellers come together to exchange goods and services. They consist of several key components:
-
-*Buyers
Individuals or organizations seeking to purchase goods or services.
-*Sellers
Individuals or organizations offering goods or services for sale.
-*Goods or services
Tangible or intangible items being traded.
-*Prices
The monetary value assigned to goods or services.
Markets can be classified into different types based on their characteristics:
-
-*Perfect competition
A market with numerous buyers and sellers, where no single entity has significant market power.
-*Monopoly
A market dominated by a single seller, who controls a significant portion of the supply.
-*Oligopoly
A market with a small number of large sellers, who collectively control a significant portion of the supply.
Market Forces
Market prices are determined by the interaction of supply and demand.
-
-*Supply
The amount of goods or services that sellers are willing and able to offer at a given price.
-*Demand
The amount of goods or services that buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
Factors such as technology, consumer preferences, and government regulations can affect supply and demand, leading to price fluctuations. For instance, technological advancements can increase supply and lower prices, while changes in consumer tastes can shift demand and affect market equilibrium.
Market Structures
Market structure refers to the number and size of buyers and sellers in a market, and how they interact. Different market structures have distinct implications for competition, pricing, and consumer choice:
-
-*Perfect competition
Numerous buyers and sellers, no single entity has significant market power.
-*Monopoly
A single seller controls a significant portion of the supply.
-*Oligopoly
A small number of large sellers collectively control a significant portion of the supply.
-*Monopolistic competition
Many sellers offer differentiated products, with some degree of market power.
Market Failures

Markets can sometimes fail to allocate resources efficiently, leading to outcomes that are not socially optimal. Market failures include:
-
-*Monopolies
A single seller has significant market power, leading to higher prices and reduced consumer choice.
-*Externalities
Costs or benefits of production or consumption that are not reflected in market prices.
-*Information asymmetries
Buyers and sellers have unequal access to information, leading to market inefficiencies.
Government interventions, such as antitrust laws and regulations, aim to address market failures and promote competition and consumer welfare.
Commonly Asked Questions: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Markets
What are the key components of a market?
Markets are characterized by buyers, sellers, a traded good or service, and a mechanism for determining prices.
How do supply and demand interact to influence market prices?
Supply and demand are two fundamental forces that determine the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall, and when demand exceeds supply, prices tend to rise.
What are the different types of market structures?
Common market structures include perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition, each characterized by varying degrees of competition and market power.