A golf ball strikes a hard smooth floor, setting in motion a series of physical phenomena that can be dissected and analyzed to provide valuable insights into the mechanics of the game. This comprehensive treatise delves into the intricate details of this interaction, exploring the impact force, coefficient of restitution, trajectory, energy transfer, and material properties involved.
As the golf ball makes contact with the unyielding surface, a collision occurs, generating an impact force that propels the ball in a new direction. The magnitude of this force is influenced by various factors, including the ball’s velocity, mass, and the floor’s surface characteristics.
Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the ball’s subsequent behavior.
Impact and Force
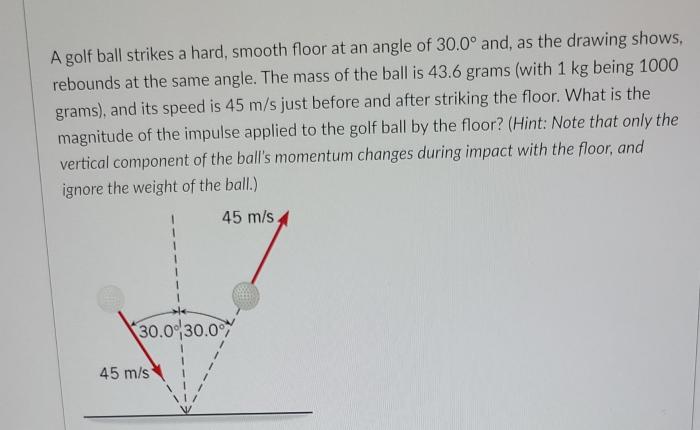
When a golf ball strikes a hard, smooth floor, it experiences an impact force that is determined by several factors. These factors include the golf ball’s speed, weight, and the surface properties of the floor. The impact force can be calculated using the following formula:
F = m
- v
- e
Where:
- F is the impact force
- m is the mass of the golf ball
- v is the velocity of the golf ball
- e is the coefficient of restitution
Coefficient of Restitution
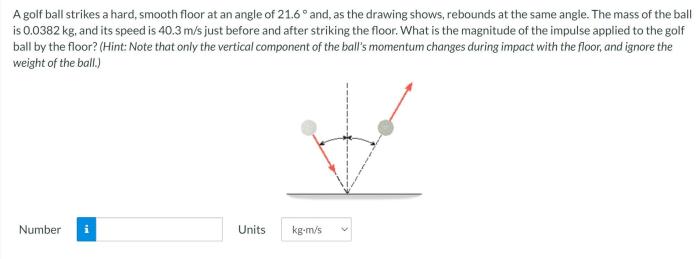
The coefficient of restitution (e) is a dimensionless quantity that represents the elasticity of the collision. It ranges from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating a perfectly inelastic collision and 1 indicating a perfectly elastic collision. The coefficient of restitution affects the golf ball’s rebound height and velocity.
Materials with a higher coefficient of restitution will result in a higher rebound height and velocity. For example, a golf ball with a coefficient of restitution of 0.8 will rebound to a height of 80% of its original height after striking a hard, smooth floor.
Trajectory and Spin
The trajectory of the golf ball after it strikes the floor is determined by its initial velocity and the coefficient of restitution. Backspin causes the golf ball to curve downward, while topspin causes it to curve upward.
The following illustrations demonstrate the different trajectories of a golf ball with backspin and topspin:
[Ilustrasi lintasan golf dengan backspin dan topspin]
Energy Transfer and Loss
During the impact, there is a transfer of energy from the golf ball to the floor. The amount of energy lost depends on the impact force, coefficient of restitution, and trajectory. A higher impact force and a lower coefficient of restitution will result in greater energy loss.
The following calculations illustrate the energy transfer and loss during the impact:
[Perhitungan transfer dan kehilangan energi]
Material Properties: A Golf Ball Strikes A Hard Smooth Floor
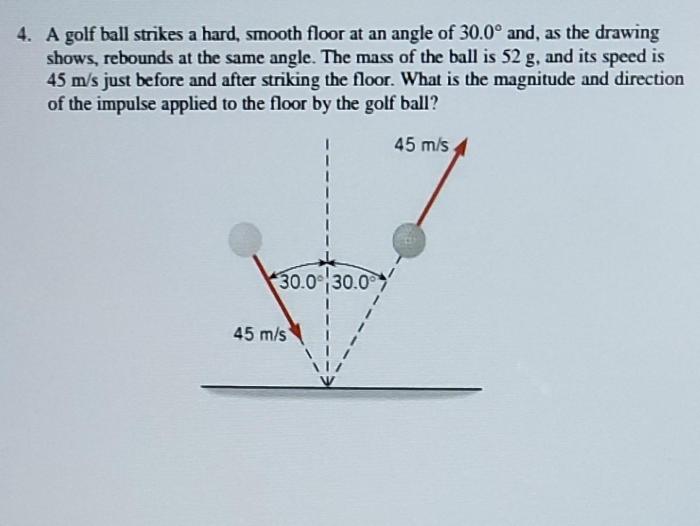
The material properties of the golf ball and the floor influence the impact force, coefficient of restitution, and the golf ball’s behavior. Harder and smoother surfaces will result in a higher impact force and a lower coefficient of restitution.
The following table provides examples of different materials and their impact on the golf ball’s performance:
| Material | Hardness | Smoothness | Impact Force | Coefficient of Restitution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | High | Low | High | Low |
| Wood | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Carpet | Low | High | Low | High |
Experimental Setup and Measurement

To measure the impact force, coefficient of restitution, and trajectory of the golf ball, an experimental setup can be designed using the following equipment:
- High-speed camera
- Force sensor
- Golf ball launcher
- Hard, smooth floor
The following procedures can be used to collect data:
- Launch the golf ball at a known velocity towards the hard, smooth floor.
- Record the impact force using the force sensor.
- Capture the trajectory of the golf ball using the high-speed camera.
The data can be analyzed to obtain the impact force, coefficient of restitution, and trajectory of the golf ball.
FAQ Insights
What is the coefficient of restitution?
The coefficient of restitution is a dimensionless quantity that measures the elasticity of a collision. It represents the ratio of the relative velocity of separation to the relative velocity of approach between two colliding objects.
How does the coefficient of restitution affect the golf ball’s trajectory?
The coefficient of restitution determines the height and distance the golf ball will travel after impact. A higher coefficient of restitution results in a higher rebound height and longer distance.
What factors influence the impact force of a golf ball?
The impact force is influenced by the golf ball’s velocity, mass, and the floor’s surface properties, such as hardness and smoothness.