Mitosis vs meiosis worksheet answers – Embark on a journey into the captivating realm of cell division as we explore the intricacies of mitosis and meiosis. Through this comprehensive guide, you’ll unravel the mysteries behind these fundamental processes, gaining a deeper understanding of their roles in growth, reproduction, and genetic diversity.
Delving into the core differences and similarities between mitosis and meiosis, we’ll illuminate the significance of each stage and its impact on the genetic makeup of cells. Discover how these processes contribute to the development and maintenance of life.
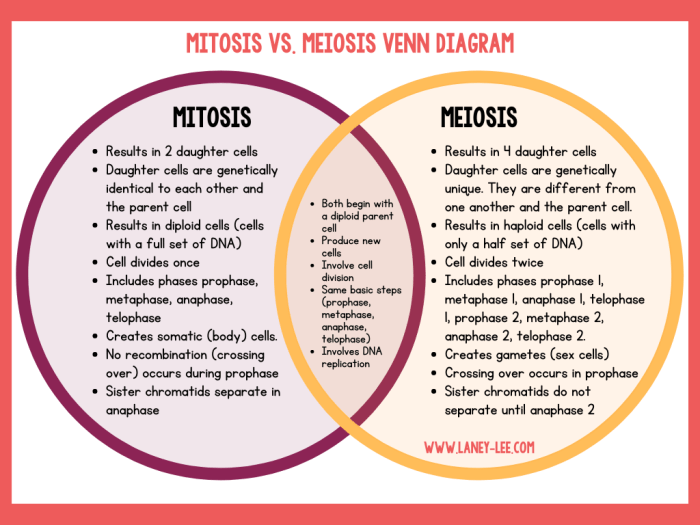
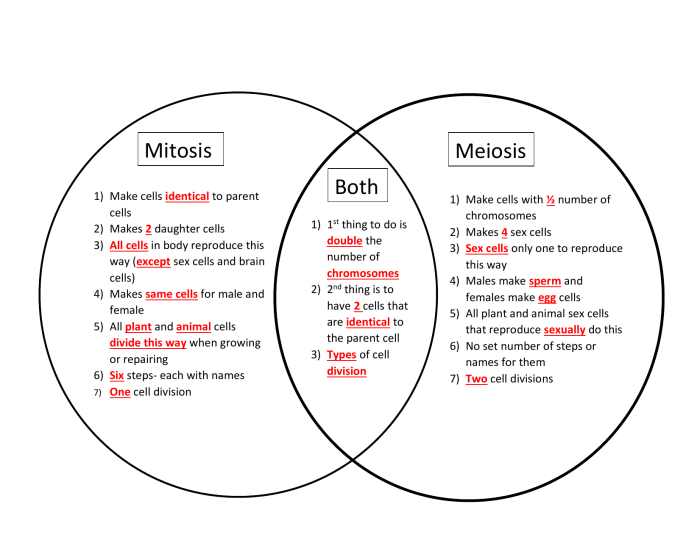
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis: Mitosis Vs Meiosis Worksheet Answers
Mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that serve different purposes in the life cycle of eukaryotic organisms.
Mitosis is a process of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. It is used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a process of cell division that produces four haploid daughter cells from a single diploid parent cell.
It is used for sexual reproduction.
The following table compares the key characteristics of mitosis and meiosis:
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of divisions | 1 | 2 |
| Chromosome number | Diploid (2n) | Haploid (n) |
| Purpose | Growth, repair, asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
Mitosis and meiosis are similar in that they both involve the division of a cell into two or more daughter cells. However, they differ in the number of divisions, the chromosome number, and the purpose of the division.
Stages of Mitosis
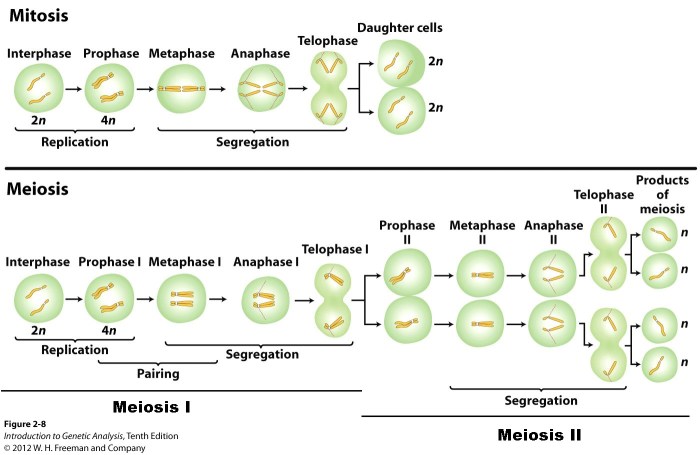
Mitosis is divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophaseis the first and longest stage of mitosis. During prophase, the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. The spindle fibers begin to form and attach to the chromosomes.
Metaphaseis the second stage of mitosis. During metaphase, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. The spindle fibers are attached to the chromosomes at their centromeres.
Anaphaseis the third stage of mitosis. During anaphase, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the chromosomes apart.
Telophaseis the fourth and final stage of mitosis. During telophase, the chromosomes reach the poles of the cell and the nuclear envelope reforms. The spindle fibers disappear and the cell divides into two daughter cells.
Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis is divided into two stages: meiosis I and meiosis II.
Meiosis Iis the first stage of meiosis. During meiosis I, the chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. The chromosomes then line up in the center of the cell and the spindle fibers attach to them.
The chromosomes then separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Meiosis IIis the second stage of meiosis. During meiosis II, the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell and the spindle fibers attach to them. The chromosomes then separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. The cell then divides into four haploid daughter cells.
The following table compares the stages of meiosis I and meiosis II:
| Stage | Events |
|---|---|
| Meiosis I |
|
| Meiosis II |
|
Genetic Variation
Meiosis is an important source of genetic variation in sexually reproducing organisms. Crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis result in the production of gametes that are genetically unique.
Crossing overis a process that occurs during meiosis I in which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This results in the production of gametes that contain a unique combination of alleles.
Independent assortmentis a process that occurs during meiosis I and meiosis II in which the chromosomes line up independently of each other. This results in the production of gametes that contain a unique combination of chromosomes.
The combination of crossing over and independent assortment ensures that the offspring of sexually reproducing organisms are genetically unique.
Applications of Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are essential processes for the life of eukaryotic organisms.
Mitosisis used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. Growth occurs when cells divide and increase in number. Repair occurs when cells are damaged and need to be replaced. Asexual reproduction occurs when a single organism produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
Meiosisis used for sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction occurs when two organisms combine their gametes to produce offspring that are genetically unique. Meiosis is essential for the maintenance of genetic diversity in populations.
FAQ
What is the primary distinction between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis generates four genetically diverse daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
Why is crossing over crucial during meiosis?
Crossing over shuffles genetic material between homologous chromosomes, leading to genetic recombination and increased genetic diversity.